China borders reopening in 2023 marked a highly anticipated event for global trade and investments after extended travel restrictions due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The impact of COVID-19 on China’s consumption and export/import sectors has been profound, with citizens opting for essential goods and online shopping. China’s monetary and fiscal policies, as well as the manufacturing, travel, and housing sectors, are all affected by the pandemic.
However, the question is, will reopening provide the anticipated economic boost? The pandemic had a significant impact on the Chinese economy. So let’s take a closer look to understand the effect of COVID and the changes coming through China borders reopening.
The Chinese citizens transitioned to substantial savings
Chinese households have increased savings from 17% to 33% of their income due to economic uncertainty rather than pent-up demand caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
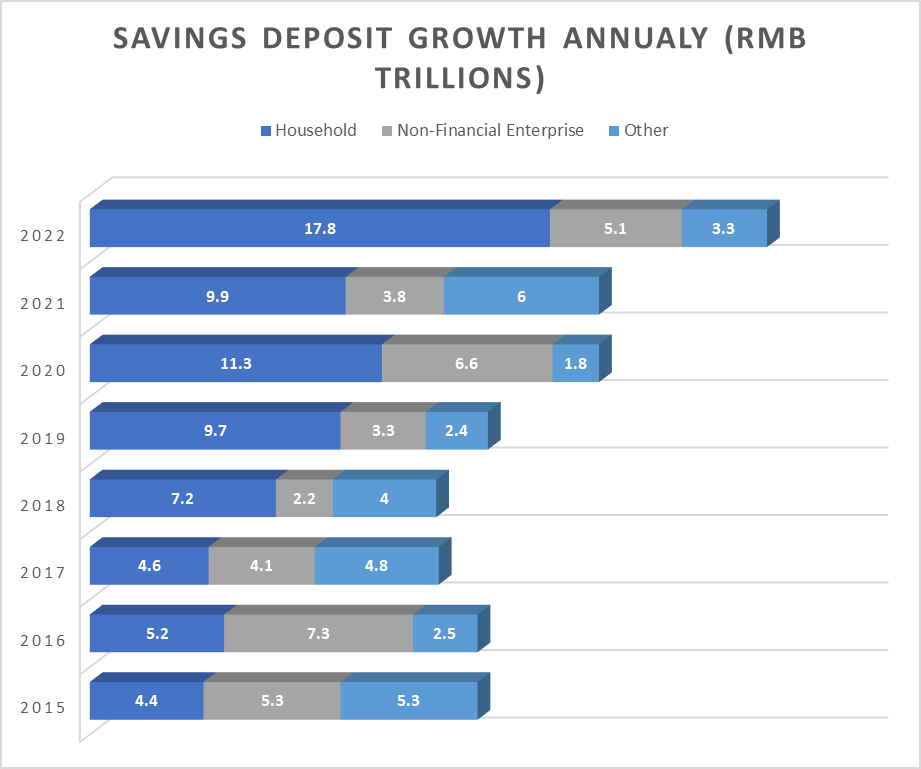
According to recent data from China’s central bank, Chinese bank deposits increased by 26.3 trillion Chinese yuan ($3.9 trillion) in 2022, with household savings accounting for 17.8 trillion yuan. China’s strict COVID-19 containment measures drove the increase in savings as it forced many people to remain indoors for long periods, resulting in suppressed consumer spending.
While some excess savings could be spent as “revenge spending,” a significant portion reflects Chinese households’ preference for precautionary savings in bank deposits and housing investments.
Even if consumer spending returns to normal, the uncertainty in the economy could prevent Chinese households from investing in housing or stocks, causing bank deposits to remain high. A household survey by the People’s Bank of China during Q3 of 2022 showed that only 22.8% of respondents wanted to buy more things, while 58.1% preferred to increase their savings.
Although consumption is expected to recover in 2023, Chinese households may maintain higher precautionary savings in the long term due to mounting economic uncertainty.
To encourage spending, the Chinese government must address the cost-of-living crisis that has made Chinese consumers reluctant to spend. This can be achieved by making housing affordable in major cities, offering welfare benefits for low- and middle-income families, and increasing social protection. Excessive household savings could severely impede China’s long-term economic prospects without significantly overhauling its fiscal policy and tax system.
China’s consumption faced a crushing blow in 2022.
In 2022, China’s consumption suffered a significant blow, leading to a surge in excess savings. However, the situation appears to be improving with the country’s mobility index improving and major cities offering consumption vouchers to tap into the pent-up spending desire of consumers.
The graph below shows a decline in total retail sales between 2021-2022.
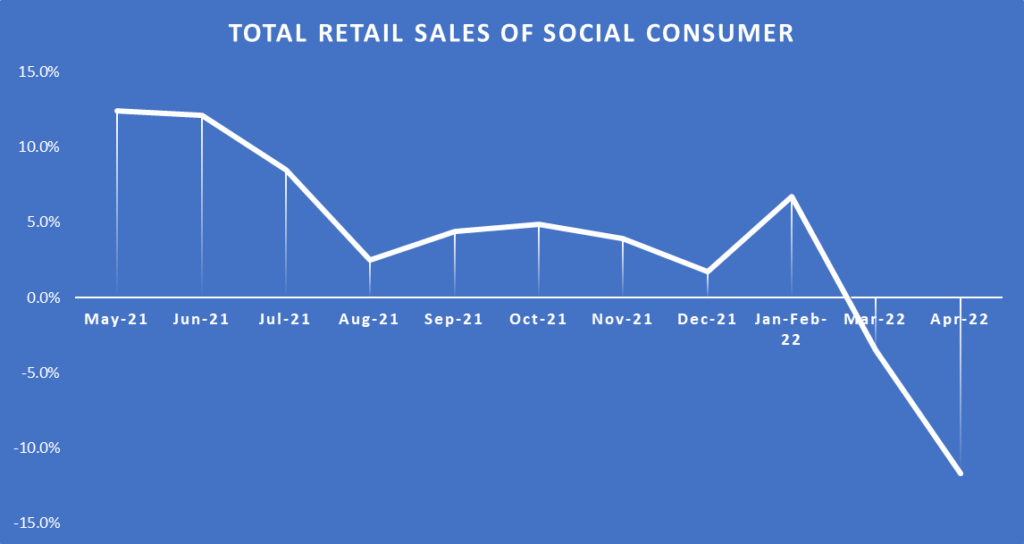
Beijing has also decided to provide cash subsidies to around 300,000 low-income residents to counter the impact of high food prices. Despite this, consumers seem cautious due to the prevailing economic uncertainty, which has impacted household borrowing demand. The data shows a decline in new loans, condo transactions, and new mortgages, with money trapped in banks, leading to a growing gap between deposits and loans.
China’s trade: A pandemic-proof powerhouse?
Imports and exports remained resilient during the pandemic, only slightly dipping towards the end of 2022. Despite the setbacks, they outperformed pre-COVID levels, highlighting the country’s economic prowess.
The graph presented below shows the movement of China’s trade between 2017 to 2022.
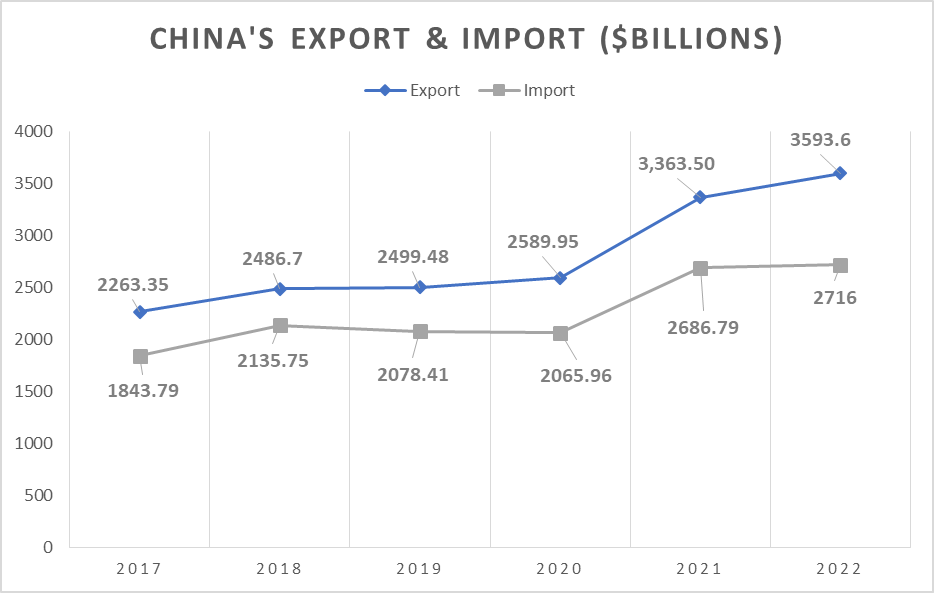
As China’s borders reopen, the import and export trade is expected to hold steady, paving the way for promising economic growth.
Will the monetary and fiscal policies support economic recovery with China borders reopening?
With China borders reopening, monetary and fiscal policies are critical for the government to manage its economy and ensure stability. According to a recent Reuters report, China’s economy is expected to rebound in 2023, driven by a substantial expansion in domestic demand. China’s accommodative fiscal and monetary policies will likely support this growth, designed to spur economic activity and support businesses.
On the fiscal side, the Chinese government has introduced targeted stimulus measures such as tax cuts and infrastructure spending to support businesses and households. The government aims to boost consumer spending and increase investment in critical sectors of the economy.
The People’s Bank of China has implemented monetary policies such as cutting interest rates and reducing reserve requirements for banks to encourage lending and boost liquidity. In 2022, China’s monetary policies included profit transfer to the government, reserve requirement ratio (RRR) cuts, loan prime rate (LPR) cuts, re-lending programs, and medium-term lending facility (MLF) rate adjustments.
In March 2022, the PBOC announced an RMB 1 trillion profit transfer to support local businesses and people. Additionally, RRR and LPR cuts freed up funds for banks to provide more loans to struggling businesses. The People’s Bank of China (PBOC) also launched re-lending programs worth RMB 100 billion for the transport industry and RMB 40 billion for elderly care. The MLF is a critical channel through which the PBOC can inject liquidity into the banking system.
In January 2022, the PBOC reduced the MLF rate to 2.85% on one-year MLF loans worth RMB 700 billion. In addition, in May 2022, the PBOC cut the five-year LPR by a record amount, from 4.6% to 4.45%, to help boost the property sector. These measures aim to increase credit availability and lower borrowing costs for businesses.
China’s policymakers are expected to maintain an accommodative stance to support economic recovery and promote sustainable growth as the country’s borders continue to reopen. China’s policy measures can help to drive economic growth and maintain financial stability in the post-pandemic era by providing targeted support to businesses and households.
China’s monetary and fiscal policies are critical tools that will play a significant role in driving economic growth and maintaining financial stability as the country reopens its borders and emerges from the pandemic.
China’s Manufacturing, Travel, and Housing
Manufacturing: China’s manufacturing sector showed improvement in January as the Caixin/S&P Global manufacturing purchasing managers’ index rose to 49.2, up from 49.0 in December. However, the official PMI survey reported a better-than-expected reading of 50.1, possibly due to its focus on larger state-owned businesses.
Travel: Domestic travel within China is recovering, with 308 million tourism trips made during the recent Lunar New Year period, a recovery to 88.6% of 2019 levels. International travel remains slow, with airlines only offering 11% of 2019 capacity levels, expected to increase to 25% by April.
Housing: Falling home prices, sales, and investments are pressuring China’s economy, with the property market likely to remain weak due to sluggish income expectations and concerns about home delivery. The government is attempting to support the industry by lifting a ban on fundraising via equity offerings for listed property firms. Still, the decline in home prices has become broader, with prices falling in 68 cities on December 22 compared to 57 cities on November 22.
Final Words
China’s borders reopening and travel restrictions being lifted, consumer spending could increase, but economic instability and income disparity may continue influencing people’s buying patterns. The government’s efforts to provide social protection and stimulate expenditure may be beneficial, but individual attitudes and preferences will determine the outcome.
As you can see, there are both pro and con arguments for China borders reopening. The country can alter the global economy significantly. Will China, strengthen or weaken the global economy? Only time will tell.
FAQs
How might China’s border reopening impact global inflation?
According to the Swiss Re Institute research, China’s border reopening may slow the expected decline in global inflation because it could increase demand for goods and services, pushing up prices. This effect could be significantly pronounced if China’s reopening spurs a broader economic recovery.
What are the potential spillover effects of China’s border reopening on commodity prices?
Swiss Re Institute’s research suggests that reopening China’s borders could spillover effects on commodity prices. Specifically, it could increase demand for oil, metals, and agricultural products, increasing prices. This effect could be significantly pronounced if China’s robust economic recovery significantly increases demand.
How might China’s border reopening affect the pace of economic recovery in the global economy?
China’s border reopening could positively and negatively impact global economic recovery. It could increase demand, boosting exports and growth in other countries. However, there is a risk of a COVID-19 resurgence, harming growth. Moreover, a slower-than-expected recovery in China could also dampen global growth prospects.
Read more: How Long-term investing helps create life-changing wealth – TOI.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 3
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.