Amid the rising interest rates, chatter around the impending recession in 2023 is slowly gaining strength. And, with recent bank runs in the US and the forced merger of Credit Suisse with rival UBS, the predictions of a recession in 2023 appear to be coming true. We hope this doesn’t occur.
So, why are economists predicting recession in 2023? Let’s find out.
State of Global Financial System
The global financial system is highly complex, and economic growth is not entirely driven by corporate profits or buoyancy in government tax collections but by interest rates. Yes, you read that correctly.
In 1976, the global financial system witnessed a fundamental shift when US President Nixon ordered moving away from the Bretton Woods system, wherein the value of each dollar circulating in the economy was defined in gold, meaning each dollar in circulation was backed by gold and turned the monetary system into a flat one.
The dollar’s value was market determined with strict supervision of the Federal Reserve. It reduced the risk of overburdening the system with gold, allowing the government to raise more debt to fuel the country’s economic growth.
Since then, the global financial system has become heavily debt-driven. The total public debt as a percentage of GDP in the US had reached 120% by the end of 2022. Over $23.9 trillion in US treasury securities are outstanding in the market. It is also true for most developed economies.
Even a small percentage change in the interest rates can impact the stability of various economies. So, a delicate balance is needed when changing interest rates at regular intervals to avoid an inflationary situation without affecting the growth levels.
Inverted Yield Curve Has Economists Predicting Recession
When economies are overdependent on debt, the chances of economic accidents are always high, which can derail global economic growth. An inverted yield curve is one such financial accident. Usually, the return on long-term debt paper should always be higher than short-term debt papers in all circumstances, as long-term holders assume more risk by locking their money for longer.
But, when the yield on short-term debt papers exceeds that of long-term debt papers because of multiple rate hikes at short intervals, it results in an inverted yield curve.
An inverted yield curve occurs when the yield on 2-year Treasury securities exceeds the yield on 10-year Treasury securities in the market. As market participants become pessimistic about the economy’s outlook, demand for longer-dated bonds increases, driving down the yield.
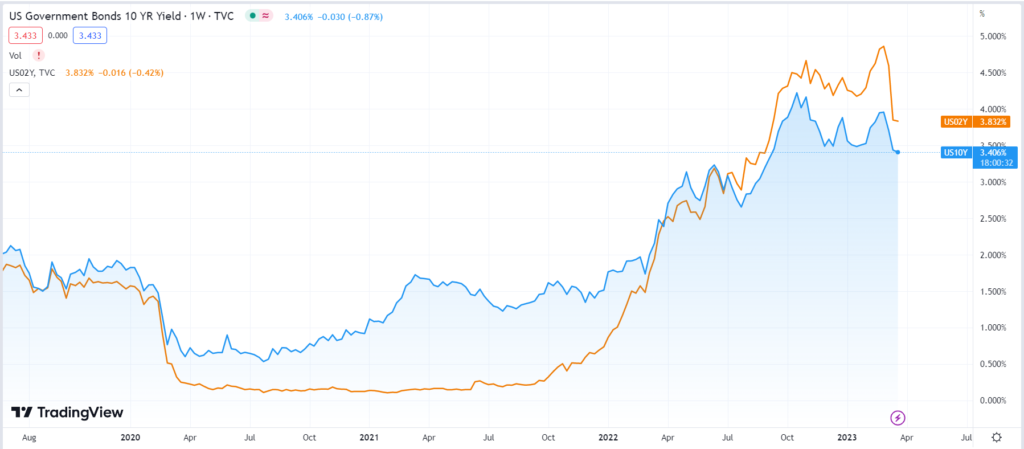
The chart above shows that yield on 2Y US Government Bonds exceeded 10Y papers around July last year and continues to be in an inverted state. For example, at the start of March 2023, the 10-Y yield was around 4%, and the 2-Y yield was about 4.8%.
In 2023, the yield curve witnessed the deepest inversion since 1981.
Furthermore, as the yield on 2Y US bonds increases, the market value of previously issued 10Y bonds on lower rates falls, resulting in long-term holders of the debt paper suffering significant mark-to-market (MTM). It is one of the few reasons why the SVB and Signature Bank in the US collapsed.
Does an Inverted Yield Curve Indicate an Impending Recession?
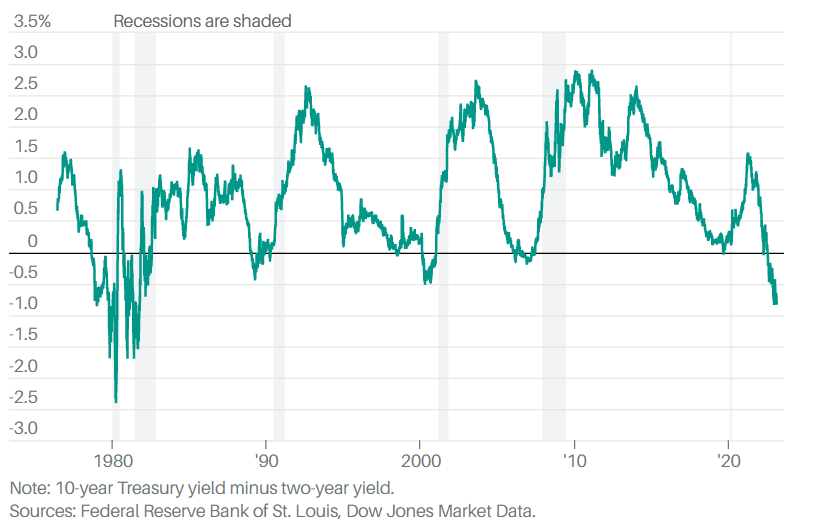
An Inverted Yield Curve is not ideal for any economy as it destabilizes the debt market. Whether an inverted yield curve indicates, an impending recession is a much-debated topic. However, looking at the past will show that an economic slowdown always follows a yield inversion.
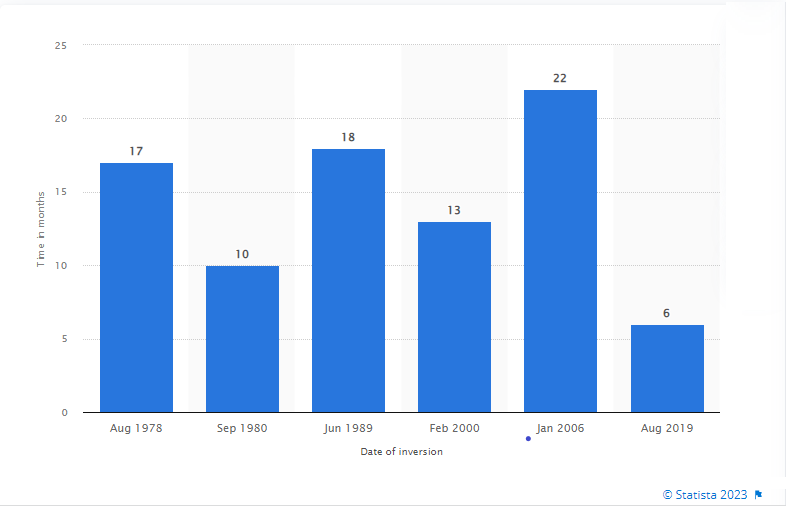
Since 1978, the global financial system has witnessed six yield curve inversions, and the gap between the start of inversion and recession ranged between 6 to 22 months. For instance, the 2008 global financial crisis happened 22 months after the first inversion of the yield curve was reported.
Number of months between yield curve inversion and the start of recession 1978-2022
Why does an Inverted Yield Curve indicate a Recession?
In an inverted yield curve scenario, investors’ expectation in the long term decline and tries to focus and profit from short-term bets. Similarly, businesses also put their long-term expansion plans on hold due to the evolving conditions, resulting in little demand for long-term funds. Therefore, overall demand takes a massive hit.
With the wider spread, the chances of an impending recession grow, and because of the pessimism surrounding the market gives way to fear that increases the likelihood of a recession.
Given the current global economic trajectory, where IMF has projected global growth to slow down to 2.9% in 2023 from 3.4% in 2022, which is why economists predicting recession is inevitable in 2023. In a WSJ survey in Jan 2023, economists have put a 61% probability of a recession in 2023.
FAQs
What is an inverted yield curve?
An inverted yield curve happens when short-term government bond yields exceed long-term government bond yields.
Does yield curve inversion indicate a recession?
Yes, yield curve inversion indicates a recession. For every downturn since 1978, yield curve inversion took place at least six months to one year before.
Why does yield curve inversion impacts economic growth?
Due to higher borrowing costs, businesses put a hold on their expansion plan and avoid taking risks, thus impacting overall demand.
Related investing topics
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 4.1 / 5. Vote count: 8
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

