GDP fell to 4.4% in Q3FY23, the lowest in the last three-quarters, according to data released by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI). This is unsurprising given that economists have predicted that growth momentum will slow due to decelerating economic activity in the coming quarters.
In its December 2022 meeting, the MPC forecasted real gross domestic product growth for 2022-23 at 6.8%, with Q3 at 4.4% and Q4 at 4.2%. Real GDP growth for Q1FY24 was projected at 7.1% and 5.9% for Q2.
In this article, we will explain what GDP is, how it is calculated, and what factors caused GDP growth to fall by 4% in Q3F23.
What is GDP (Gross Domestic Product)?
In simple terms, GDP, or Gross Domestic Product, is the total market value of all finished goods and services produced within a country during a given period. It is a comprehensive indicator of the country’s overall economic health and an essential tool in strategic policy-making.
If gross domestic product rises for three consecutive quarters, the economy is growing; if it drops, it is said to be shrinking. The economy is said to be in recession when Gross Domestic Product falls for two consecutive quarters.
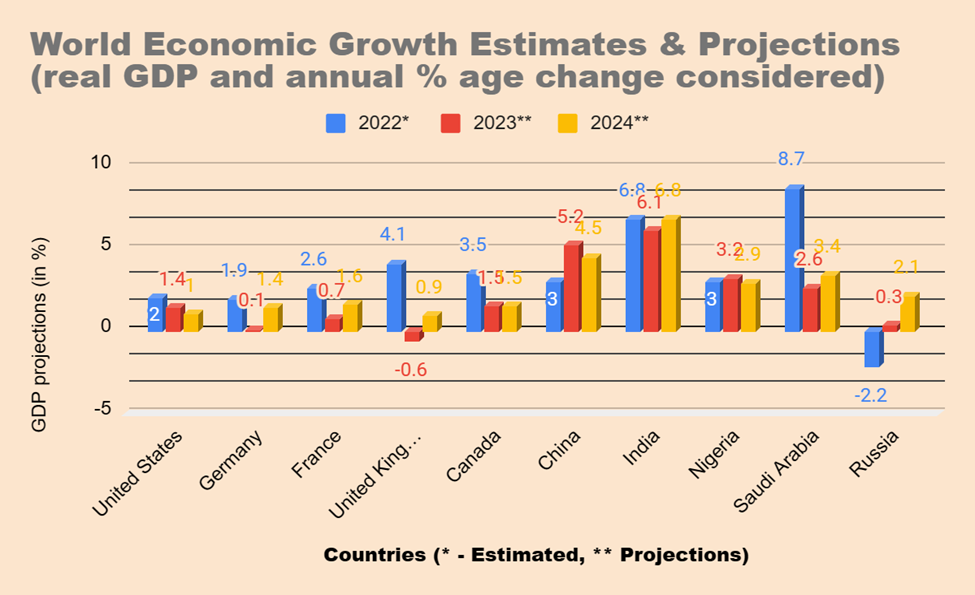
According to the most recent IMF forecast on January 23, India’s growth will slow from 6.8% to 6.1% in 2023-24 before accelerating to 6.8% in 2024-25. Among advanced, emerging, and developing economies, India’s GDP is expected to be the second highest, trailing only Saudi Arabia, thanks to the robust economic policies introduced in India.
Types of Gross Domestic Product
GDP can be classified in a variety of ways, but for your convenience, we’ve selected the most commonly used versions, which are listed below-
Real Gross Domestic Product
Real GDP is a country’s total economic output each year valued at a predetermined base year market price. It is determined and referred to using the same year’s constant US Dollar or Rupee price.
Real GDP is calculated after accounting for inflation, i.e. it is inflation-adjusted and can be compared to two or more financial years. In addition, it gives a more precise portrayal of a country’s economic performance because it exclusively considers production and is free from price changes or currency fluctuations.
Nominal Gross Domestic Product
The total economic output produced in a year valued at the current market price is called nominal GDP. Nominal GDP is expressed in absolute terms and is not inflation-adjusted. It is thus always greater than real GDP because recent price changes are considered in this case.
Instead of two fiscal years, you can compare nominal GDP with different quarters of the same year. Nominal GDP is more difficult to analyze and less reliable than Real GDP, as it is calculated at constant prices.
Gross Domestic Product per Capita
Gross domestic product per capita is a financial metric that measures the country’s economic output per person. It is derived by dividing the country’s total Gross Domestic Product (GDP) by the population. Economists use a universal tool to analyze a country’s prosperity based on its economic growth, as its components are regularly tracked globally.
When GDP per capita is calculated at the national level, it provides information about how the country’s population is expanding or contracting. When estimated globally, it gives a comparable insight into global economic prosperity and developments.
Population and Gross Domestic Product are essential for calculating a country’s per capita income. Therefore, a country with the highest GDP may not have the highest per capita because of its vast population.
Let us clarify this with the help of an illustrative example.
| Country | Country A | Country B |
| Population (in a million) | 10,000 | 20,000 |
| Gross Domestic Product (in $) | 10,00,00,000 | 15,00,00,000 |
| Gross Domestic Product per capita (in $) | 10,000 | 7,500 |
In this chart, you will find that though country B has higher GDP, its GDP per capita is lower than country A’s due to its larger population size.
Gross Domestic Product Growth Rate
GDP growth rate, also known as the Economic Growth rate, measures the country’s Real GDP increase over the previous period. The rate of change is expressed as a percentage, which indicates how quickly the economy is growing or contracting. Its growth rate is an essential tool for economists to use in determining the attractiveness of sectors and industries and the impact on employees and consumers.
A positive gross domestic product growth rate indicates economic expansion, which will help businesses, jobs, and personal income growth. However, if it is exceptionally high, it may also invite trouble because if it reaches a peak beyond that point, the bubble may burst, and economic growth will stagnate. Conversely, a negative GDP growth rate indicates a shrinking economy with no jobs or growth prospects for businesses.
How is Gross Domestic Product measured?
There are mainly three ways to calculate GDP, each of which yields the same response-
- Expenditure/Spending Approach
In this calculation method, we consider the sum of all final goods and services (including all consumer spending, government spending, business investment spending, and net exports) purchased within the country over a specific period.
- Income Approach
This approach is based on the accounting reality that all expenditures in an economy should equal the total income earned from manufacturing all economic goods and services.
The Gross Domestic Product calculation formula below calculates the net foreign factor income by subtracting the total revenue earned by a country’s citizens and businesses in foreign countries from the total income generated by foreign citizens and businesses in that country.
- Output Approach
This gives you an idea of the output or production in the country. In this method, you arrive at gross domestic product by adding the gross value of various goods and services with taxes less the subsidies on the products.
| Expenditure/Spending Method | Income Method | Output/Production Method | |
| Formula | Consumer Spending + Investments + Government spending + Net exports (= Total exports- total imports) | Total national income + total Sales tax + depreciation of assets + Net Foreign Factor Income | The total value of goods and services – value of intermediaries or intermediate costs |
Five Factors that Led to the Fall in Gross Domestic Product
- High Inflation Amid Low Growth
The upward trend in global inflation has significantly impacted commodity markets, global financial markets, and constant supply chain pressures. These factors, geopolitical tensions and rising oil prices, greatly influenced the GDP growth rate, which fell by 4%.
- Aggressive Monetary Tightening
To tighten the surplus liquidity sloshing around the system, RBI slowly shifted the focus of its monetary policies toward “withdrawal of accommodation”. This increased bank, repo rates, and the Cash Reserve Ratio and lending rate hikes.
- Subdued Consumption Demand
People tightened their purse strings because of the price increase, and personal consumption expenditures (PCE), which account for a large portion of the Gross Domestic Product, fell dramatically. This is due to ongoing cost-push and demand-pull pressures and lingering pandemic-induced supply chain bottlenecks.
- Low growth in Government Consumption
Government Final Consumption Expenditure (GFCE) dropped by 4.8% in Q1FY23 compared to last year. Global issues like market volatility, surging U.S. dollars, tight demand-supply balance arising from geopolitical tension, and thrust on infrastructure development posed significant headwinds to the Gross Domestic Product fall.
- A Slowdown in Manufacturing and Construction
The manufacturing sector fell 1.1% in October-December FY23 due to constantly rising input costs and selling prices, a skyrocketing rate of labor wages, and an increasing input-output gap.
The Bottom Line
With weather uncertainties looming over agricultural production, geopolitical factors, tight financial conditions, and overall inflation are all concerning factors that are still simmering. So, Gross Domestic Product growth in 2023-24 may remain unpredictable, and we must remain vigilant as the Central Bank and government take steps to keep GDP growth from falling further.
Amid growing speculation, India remains the fastest-growing economy, with the IMF projecting 5.8% growth compared to global gross domestic product estimates of 2.9%.
FAQs
What are the factors that directly impact Gross Domestic Product growth?
Fours factors directly affect the GDP growth of the economy – Consumer spending on goods and services, Business investment, Government spending, and net exports.
Does Real Gross Domestic Product fall at the time of recession, and how long does it take to recover?
Yes, GDP growth will fall during a recession, as will the following four economic indicators: income, employment, manufacturing, and retail sales. Moreover, it could take months or years for the economy to recover from the effects of the recession.
How does GDP affect the lives of citizens of the country?
A higher GDP implies more disposable income for families to spend on things that are important to them. GDP growth influences labor productivity and helps you raise your standard of living.
Read more: How Long-term investing helps create life-changing wealth – TOI.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 5
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

