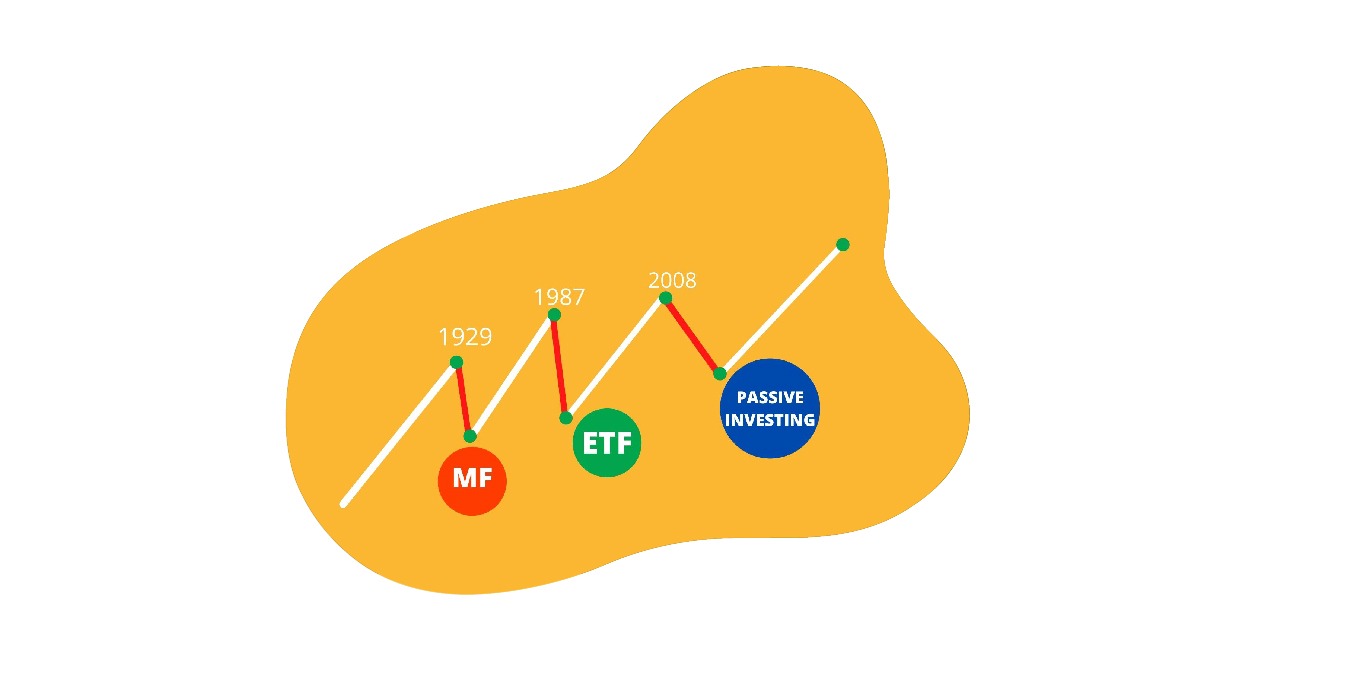
Do you ever wonder what gave rise to Mutual Funds, Exchange Traded Funds, and passive investing?
Well, we did.
We flipped through pages of history to understand what led to the invention of these investment channels or styles.
We are certain you want to know what we found. On this note, let’s begin the second chapter in the series about whether you should invest in ETFs or Equities.
The story
Very few people know that the three biggest stock market crashes are linked to the invention of modern-day Mutual Funds, Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs), and the passive investing phenomenon.
Three major economic crises that led to stock market crashes and the destruction of investor wealth shaped the investing world big time.
The Great Depression of 1929 – Mutual Funds became popular
Although modern-day Mutual Funds have existed since the early 19th -century they didn’t grab a lot of investors’ eyes until the 1980s-90s, when a few who invested in them got unbelievable returns.
Per Bianco’s research, the MFS Massachusetts Investors’ Trust in Boston marked the beginning of the Mutual Funds in 1924. The fund opened to the public in 1928.
The following years saw the launch of the first balanced fund – a combination of stocks and bonds. Called Vanguard Wellington Fund, it exists even today.
Before the great depression of 1929, there were 19 open-ended mutual funds compared to 700 closed-end funds.
You may ask, what are open-ended and closed-end funds?
An open-ended fund is a common MF you may invest in or hear about. It is a diversified portfolio that can issue an unlimited number of shares. These funds are available for repurchase and subscription continuously.
On the other hand, a closed-end fund raises capital via a one-time offering for a fixed number of shares. Investors can buy and sell these funds. However, new shares don’t get created, which means there is no new inflow into the fund.
Coming back to the story, when the stock markets crashed in 1929, highly leveraged closed-end funds could not survive during the crash. But small open-end funds survived the downfall.
The stock market crash called for new regulations in the stock markets, including the Securities Act of 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
MFs had to provide complete disclosures of their holdings and performance in the form of prospectus compulsorily because of these Acts.
India adopted MFs after three decades. The Reserve Bank of India set up Unit Trust of India (UTI) in 1963. A year later, UTI launched the first scheme called Unit Scheme (US ’64).
India’s MF Assets under Management (AUM) have grown from Rs. 6,700 crores in 1988 to Rs. 37.33 lakh crores as of Oct 31, 2021.
Black Monday Stock Market Crash of 1987 – ETFs in picture
As the name implies, it was the darkest day in the U.S. stock market history. The market gauge Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) plunged 508 points, i.e. ~23% in a single day. The drop would be equivalent to 8,104.51 points today.
Wondering how this crash is connected to the birth of ETFs launched in 1990, here is what happened.
The U.S. securities exchange launched an investigation to understand what led to such a massive sell-off. The investigation found there was no single tradeable security that represented the broad market. S&P500 had futures contracts, but there was nothing on the spot market.
The final report highlighted that an instrument representing a broader market would have reduced the impact of the stock market crash. The SEC showed an interest in building this new instrument.
Even though the U.S. SEC investigation initiated the conversation around ETFs, Canada’s Toronto Stock Exchange launched the first-ever ETF – Toronto Index Participation Fund (TIP 35) in 1990.
The U.S. got its first ETF in 1993 with the Standard & Poor’s 500 Depository Receipts (SPDRs), which tracked the performance of the S&P500 index.
India caught onto the idea quickly. Benchmark Mutual Fund launched the Nifty ETF Fund to track the performance of the Nifty50 index in 2001.
Global Financial Crisis 2008 – Passive Investing begins
Everyone knows how the collapse of Lehman Brothers in September 2008, resulted in the Global Financial crisis. The crisis not only took the financial markets down, but investors also questioned the benefit of active management.
This stock market crash paved the way for passive investing. Consistent underperformance of active funds and lower expense of passive investing attracted more investors to ETFs. Their popularity has surpassed that of MFs.
Need sound advice on where to invest, how much to invest, and for how long to invest in the stock market? Subscribe to 5 in 5 Wealth Creation Strategy and get a portfolio of 20-25 fundamentally strong stocks tailored for your goals and risk-taking ability.
*Disclaimer: The information mentioned in this email is for educational purposes. Please do not consider it a recommendation to buy/sell/hold from Research & Ranking.
Read more:
Exchange-Traded Funds – What Are They?
ETFs – Know What Makes Investing In ETFs Difficult
ETFs Or Stocks – Find Out Which One To Invest In Now
Read more: How Long-term investing helps create life-changing wealth – TOI.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 0 / 5. Vote count: 0
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
I’m Vinay Mahindrakar, an experienced content creator with
an affinity for writing on personal finance and other financial content. I
love to write on equity investing, retirement, managing money, and more.
-
Vinay Mahindrakarhttps://www.equentis.com/blog/author/vinay/
-
Vinay Mahindrakarhttps://www.equentis.com/blog/author/vinay/
-
Vinay Mahindrakarhttps://www.equentis.com/blog/author/vinay/
-
Vinay Mahindrakarhttps://www.equentis.com/blog/author/vinay/